Revising chapter 2
TELEPHONY 2
Telephony 2
Pages - Menu
How to Calculate Line Speed Or Bit Rate For One Channel.
How to Calculate Line Speed Or Bit Rate For One Channel.
Before that, I will tell you about Nyquist Theorem:
-In 1993, Harry Nyquist derived the minimum sampling frequency required to extract all information in a continuous, time-varying waveform.
-The Nyquist sampling theorem establishes the minimum sampling rate(fs) that can be used for a given PCM signal. For a sample to be reproduced accurately in a PCM receiver, each cycle of the analog input signal (Fmax) must be sampled at least twice.
-So, the sampling theorem states that for a limited bandwitch (band limited) signal with maximum frequency Fmax the equally spaced sampling frequency (Fs) must be greater than twice of the maximum frequency Fmax:
Sampling rate, fs = 2(fmax)
Example Question :
The human voice normally contains frequencies from 0 to 4000Hz. According to Nyquist Theorem, the sampling frequency (fs) is normally chosen to be twice of the highest frequency of a human voice and line speed or bit rate for one channel.
Answer:
Sampling rate, fs = 2fmax
= 2 x (4000 Hz)
=8000Hz
line speed or bit rate for one channel= sampling rate x 8bit
=8000 Hz x 8bit
= 64000bps
=64 kbps
Why we use 8 bit?
One bytes of data is transmitted during the time interval assigned to a particular channel. One channel transmits 8 bits and the halts (stop) while the next channel transmit 8 bits. The third channel then transmits its data word and so on.
Based On:
Politeknik Ibrahim Sultan Noted
By
Miss Rohana Binti Hasan.
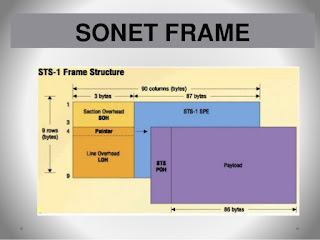
Definition and Characteristic of SONET
SONET is the American National Standards Institute standard for synchronous data transmission on optical media. The international equivalent of SONET is synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH). Together, they ensure standards so that digital networks can interconnect internationally and that existing conventional transmission systems can take advantage of optical media through tributary attachments.
SONET provides standards for a number of line rates up to the maximum line rate of 9.953 gigabits per second (Gbps). Actual line rates approaching 20 gigabits per second are possible. SONET is considered to be the foundation for the physical layer of the broadband ISDN (BISDN).
Asynchronous transfer mode runs as a layer on top of SONET as well as on top of other technologies.
SONET defines a base rate of 51.84 Mbps and a set of multiples of the base rate known as "Optical Carrier levels (OCx)."
INTRODUCTION OF
MULTIPLEXING
-
PROCESS OF SIMULTANEOUSLY TRANSMITTING TWO OR
MORE INDIVIDUAL SIGNALS OVER A SINGLE COMMUNICATION CHANNEL OR LINK.
·
MUX:
MULTIPLEXER
·
DEMUX:
DEMULTIPLEXER
FDM and WDM :
-
Used
to deal with analog information
-
Individually
signal to be transmitted are assigned a different frequency or wavelength within
a common bandwidth.
TDM :
-
Used
for digital information
-
Multiple
signals are transmitted in a different time slot.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)